Project Background: Sustainable Future
Problems Associated With Energy and the Environment
Energy and the environment are two of the biggest problems mankind faces this century. Population levels are increasing globally and energy consumption is rising rapidly as the economies of the developing world industrialise, whilst energy resources are being depleted. As demand increases, costs rise and this drives demand for lower cost forms of energy. Currently, this demand is largely met using fossil fuels, which are dirty, pollutant rich fuel sources in finite supply and are causing significant damage to the environment.
The world’s current energy mix and heavy dependence on fossil fuel energy is clearly unsustainable: both environmentally and economically.
Climate Change
Alternative Forms of Energy Production
The commitment to various pieces of legislation and the requirement for secure forms of energy has acted as a key driver for change and has created numerous opportunities to research and develop cleaner, alternative forms of meeting the global energy requirement and averting the looming energy crisis.
As a result, this has reinstated the requirement for nuclear power, in addition to encouraging further research, development and continued investment into renewable forms of energy production: including solar photovoltaics, wind, hydro, wave, and tidal to name but a few.
Possible Renewable Technology - Wind Resource
One potential renewable technology is wind power. Wind is a relatively mature renewable technology, with an established industry and there is significant wind resource potential available globally: from conventional and thermally driven winds.
The link between wind and energy was established many centuries ago, with its initial use originating in windmills for pumping water and grain grinding. However, its exploitation to produce electricity was developed more recently: with Denmark being one of the first countries to exploit their onshore resource potential in the 1970’s, closely followed by California in the 1980’s and Europe in the 1990’s.
The industry has continued to grow rapidly and there has been significant global expansion in this area: more frequently coming from offshore wind farms in moderate depth. Surprisingly, despite this “wind power currently supplies less than 1% of the world’s electricity and yet it is the fastest growing alternative energy resource” [1].
Wind Potential in the UK
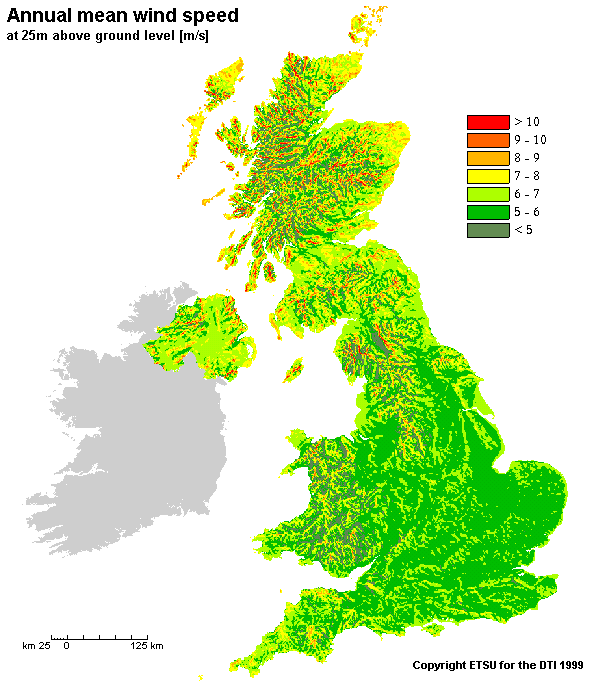
The UK is a particularly windy country, with its long exposed coastlines and low mountain ranges making the UK’s wind resource the greatest in Europe [2]. There is theoretically the potential to obtain 1000TWh of electricity each year from the wind in the UK, which is approximately three times the amount of electricity currently used in the UK per year. However, taking into consideration sensible restrictions such as protected areas and only utilising the most economic sites, there is the potential to exceed 50TWh per year on land: still providing a very significant resource.Map of the UK’s Wind Resource [3]:

The potential resource is substantial and will make a vital contribution in achieving the UK Government’s renewables targets and reducing emissions. However, there are problems associated with wind power, which must be overcome for this resource to be fully exploited.
Problems Associated With Wind Energy
Wind is not a predictable or dependant energy resource and therefore produces a very intermittent electrical output. To produce a more reliable supply of electricity; which is vital for scaling up this technology and its wider use; the electrical output must be smoothed. At present, the most common method of achieving this is using some sort of storage mechanism. This should be capable of storing electricity in times of excess supply, which can later be used to produce electricity when the wind resource is insufficient to meet demand, or the wind turbines are unable to operate.
Current storage technologies include: pumped hydro storage, compressed air energy storage, flow batteries, batteries, superconducting magnetic energy storage, supercapacitors and flywheels. However, there are several problems associated with storing electricity using these technologies.
Potential Solution & Project Proposal
An alternative storage method is to utilise a hydrogen based storage system. This would involve using a hydrogen buffering mechanism to smooth the output from the wind farm and produce a more predictable and constant supply of electricity. This buffering mechanism is an essential aspect of proving the technical feasibility of a hydrogen economy and research and development are still in the early stages, with few trials having been conducted.
Therefore, this project proposes to conduct research into a less developed field and the aim of the project is “to investigate the feasibility of utilising a hydrogen buffering scheme for a wind farm located in a remote Scottish location and a central Scottish location”. This will essentially require investigating the technical feasibility of the project, in addition to ascertaining if the project is economically viable.
References:
[1] National Georgaphic, 2005 cited in R.J. Press, K. S. V. Santhanam, M.J. Miri, A.V. Bailey & G.A. Takacs, (2009) Introduction to Hydrogen Technology John Wiley & Sons, Inc: New Jersey
[2] BERR: The UK Wind Resource http://www.berr.gov.uk/files/file17789.pdf
[3] BWEA: http://www.bwea.com/images/misc/noabl_c.gif